City of Stars
m81-01.jpg
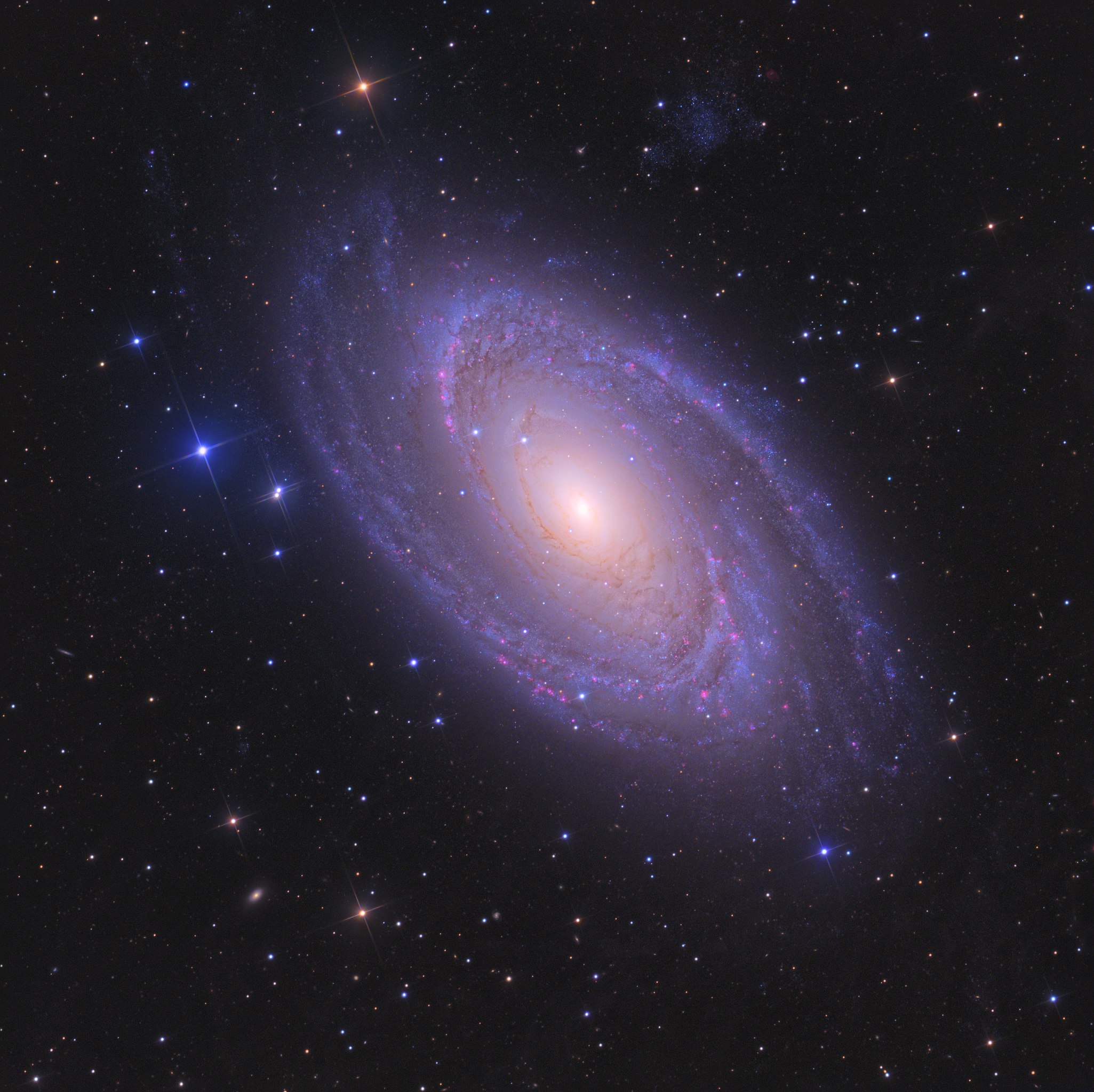
Our home galaxy, the City of Stars, as seen from Earth.
Overview
The City of Stars is a Grand Design spiral galaxy with an estimated diameter of 90,000 light years. Together with a number of smaller, proximal galaxies, the City of Stars is a member of the Celestial Adjacency group of local galaxies which, in turn, is a component of the Laniakea Supercluster.
Facts and Figures
Etymology
Calmarendians imagine their home galaxy as a dense, structured concentration of stars in the same way that an actual city is a vast, structured concentration of buildings, separated from other cities by largely empty space.
Common Framework Reference
Previous or Alternative Name(s)
The Tellurians refer to the City of Stars variously as Messier 81 (M81 for short) or Bode’s Galaxy, after the Tellurian astronomer, Johann Elert Bode, who was the first to see it from Earth.
Size
- Diameter — 90,000 light years.
- Population — 250 billion stars.
Morphological Classification
Location
Our Place in the Cosmos
Our local group of galaxies, the Celestial Adjacency, together with our near neighbours in the Andromeda Group, are located in one of the furthest reaches of the Laniakea Supercluster.
Finding Us from Earth
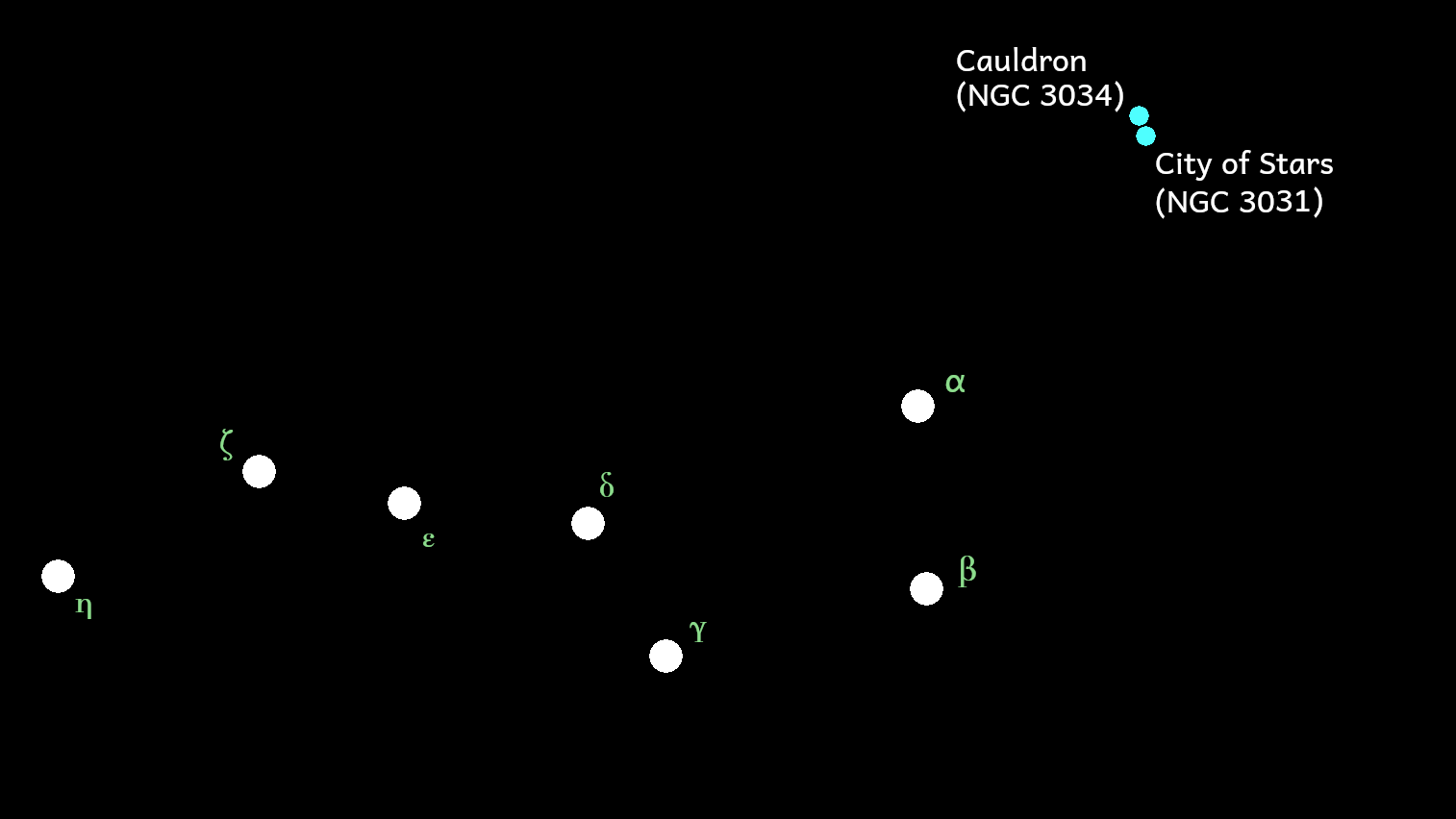
At an estimated distance of 11.8 million light years, the City of Stars and our close companion Cauldron galaxy (NGC 3034) can be found in the Ursa Major (or Great Bear) constellation of your night sky approximately 10 degrees north-west of the bright star Dubhe (Alpha Ursae Majoris). A line drawn from Phecda (Gamma Ursae Majoris) to Dubhe and extended by roughly the same distance will take you to the City of Stars. Although not visible to the naked eye except in the most favourable of circumstances, the City of Stars can be readily observed with binoculars and small telescopes.
For the more technically minded, point your telescope at the following coordinates:
- Right Ascension — 09h 55m 33.2s
- Declination — +69° 3′ 55′′
In northern locations on Earth’s surface, such as Bristol, the City of Stars never drops below the horizon so we can be seen, weather and light pollution permitting, all night, every night.




Comments